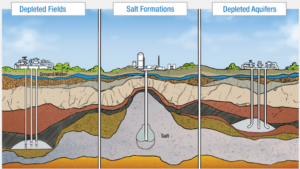
Oil and gas fields account for about 86% of gas storage capacity nationwide. The fields have been depleted of oil and gas resources and converted to receive new, processed gas for storage. The depth and geology of the fields vary across formations, but industry views them as secure storage because they are confined by an impermeable rock layer.
Oil and gas production fields have existing well heads, pipes, and other equipment that can be converted to support injection and withdrawal activities. However, older equipment and technologies now being used for storage are at risk of leaking or failing.
Regulation
After the Aliso Canyon gas storage disaster PHMSA issued new rules revising the Pipeline Safety Regulations to address safety issues related to underground natural gas storage facilities.

For More Information
- Federal Regulatory Energy Commission (FERC) overview of gas storage facilities, along with data on capacity and projects.
- Energy Information Administration (EIA) overview and data on storage capacity and projects.
- Presentation on natural gas storage operations at a Groundwater Protection Council conference.